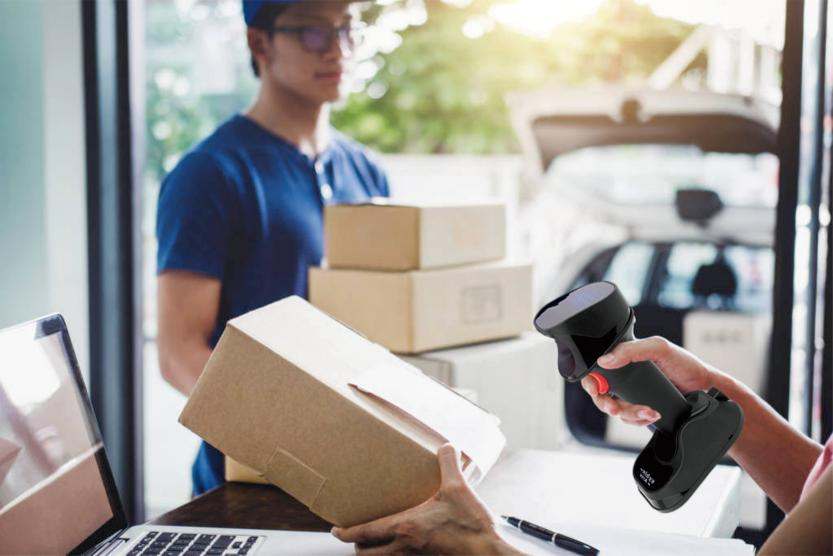
1. Preparations Before Testing
Confirm Hardware Connection: Ensure the barcode scanner is correctly connected to the host (e.g., computer, POS system) using the appropriate communication interface (e.g., RS-232, USB, RS-485).
Check Baud Rate Settings: Ensure the baud rate settings of the barcode scanner and the host are consistent, and other communication parameters (e.g., data bits, stop bits, parity bits) are also matched.
Prepare Testing Tools:
Serial Port Debugging Tools: Such as Windows' "Serial Port Debugging Assistant," Tera Term, Putty, etc.
Barcode Samples: Prepare multiple types of barcode samples for testing.
2. Methods for Testing Communication Effectiveness
(1) Using Serial Port Debugging Tools
Steps:
1.Open the serial port debugging tool and select the correct serial port (COM port).
2.Set the same baud rate, data bits, stop bits, and parity bits as the barcode scanner.
3.Scan a barcode and observe whether the serial port debugging tool receives the barcode data.
4.Check if the received data is complete, accurate, and free of garbled or missing characters.
Notes:
If no data is received, check if the hardware connection and baud rate settings are correct.
If the data is incomplete or garbled, it may be due to mismatched baud rates or interference, requiring parameter adjustments.
(2) Using Terminal Software
Steps:
1.Open terminal software (e.g., Tera Term, Putty) and select the correct communication port.
2.Set the same communication parameters as the barcode scanner.
3.Scan a barcode and observe whether the terminal interface displays the correct barcode data.
4.Check if the data is clear and error-free.
Notes:
If nothing is displayed on the terminal interface, check if the device is powered and connected properly.
If the data is abnormal, try lowering the baud rate or check if the communication line is experiencing interference.
(3) Using Barcode Scanner Companion Software
Many barcode scanner manufacturers provide dedicated configuration or testing software.
Steps:
1.Open the companion software and select the correct communication port and parameters.
2.Scan a barcode and observe whether the software interface displays the barcode data.
3.Check if the data is accurate and error-free.
Advantages: Companion software often supports automatic device status detection, making troubleshooting easier.
(4) Testing in Real Application Environments
Conduct tests in the actual usage environment to simulate real operational scenarios.
Steps:
1.Connect the barcode scanner to the actual system in use (e.g., POS system, inventory management system).
2.Scan a barcode and observe whether the system can correctly recognize and process the barcode data.
3.Check the system's response speed and data accuracy.
Notes:
If the system cannot recognize the barcode, check if the system configuration and communication parameters match.
If the response speed is slow, it may be due to a low baud rate setting or insufficient system performance.
3. Common Issues and Solutions
Issue 1: No Data Received
Possible Causes: Incorrect hardware connection, mismatched baud rate, device not powered.
Solution: Check the connection cable, confirm the baud rate settings, and ensure the device is powered.
Issue 2: Incomplete or Garbled Data
Possible Causes: Mismatched baud rate, communication line interference, incorrect data/parity bit settings.
Solution: Reconfigure communication parameters and use shielded cables to reduce interference.
Issue 3: Slow System Response
Possible Causes: Low baud rate setting, insufficient system performance.
Solution: Increase the baud rate (e.g., from 9600 bps to 19200 bps) and optimize system performance.
4. Evaluation of Test Results
Communication Stability: Whether data can be transmitted consistently and stably.
Data Accuracy: Whether the received barcode data matches the scanned barcode.
Response Speed: Whether the time from scanning the barcode to data display meets practical requirements.
Anti-Interference Capability: Whether normal communication can be maintained in complex environments (e.g., strong electromagnetic interference).
5. Summary
Testing the communication effectiveness of a barcode scanner requires comprehensive verification based on hardware connections, communication parameter settings, and real application scenarios. By using serial port debugging tools, terminal software, or companion software, communication issues can be quickly identified and resolved. In practical applications, it is also necessary to optimize the baud rate and other communication parameters based on test results to ensure stable, accurate, and efficient communication between the barcode scanner and the host.