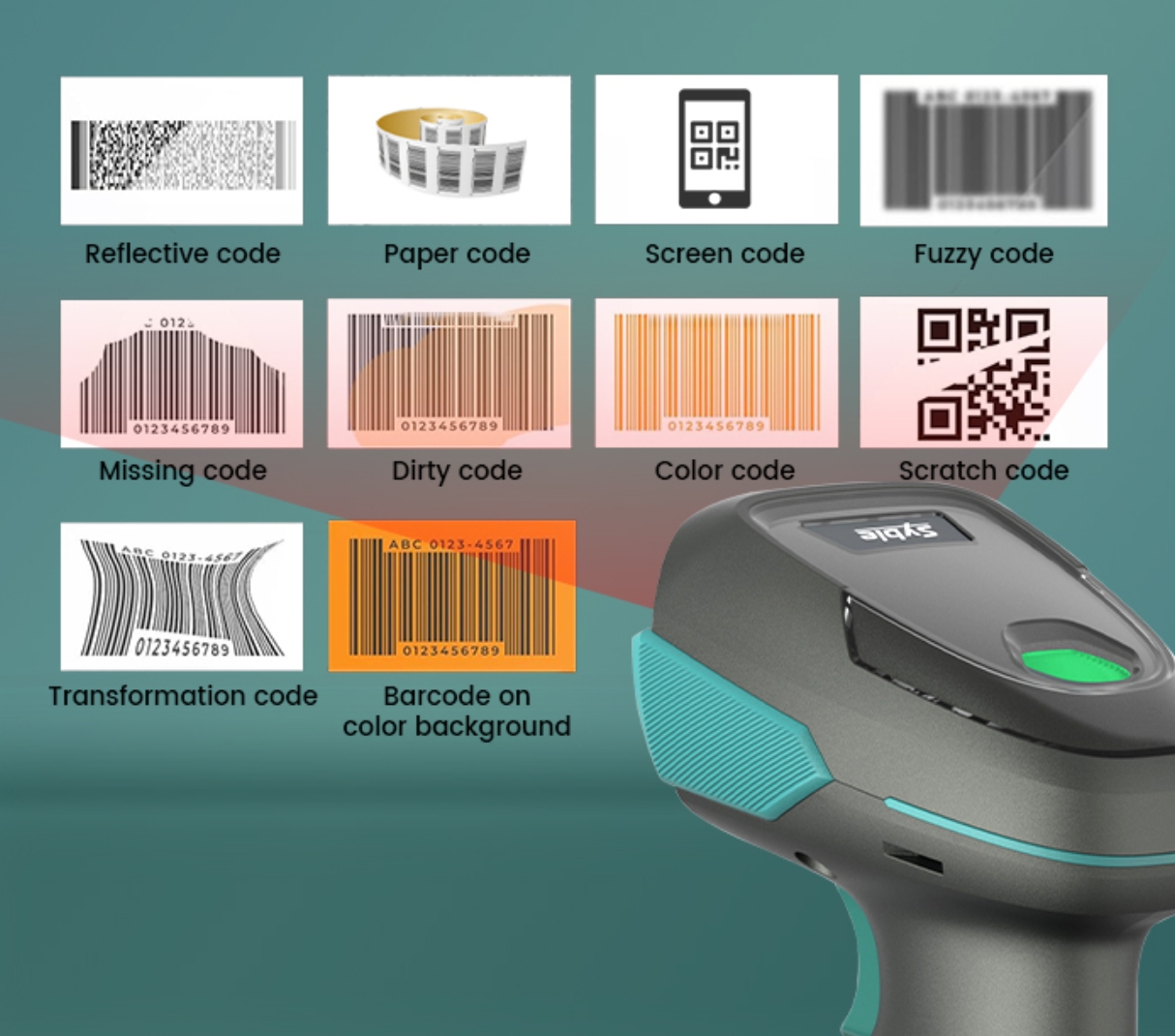
How Barcode Scanners Distinguish Between 1D and 2D Barcodes
Barcode scanners differentiate between 1D (linear) barcodes and 2D (matrix) barcodes through hardware design, decoding algorithms, and light sensing. Below are the key principles and methods:
1. Physical Structure Differences
| Feature | 1D Barcode (e.g., EAN-13, UPC) | 2D Barcode (e.g., QR Code, Data Matrix) |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Black & white stripes | Square/rectangular dot matrix |
| Data Storage | Horizontal only | Both horizontal & vertical |
| Error Correction | No error correction (damage = fail) | Built-in error correction (damage-resistant) |
2. Scanner Working Principles
(1) 1D Barcode Scanners
Laser Scanning:
Uses a laser beam to scan horizontally, detecting reflected light intensity (works only for 1D barcodes).
Linear Image Sensor:
Captures a single-line image of the barcode (similar to a smartphone camera scanning 1D barcodes).
Cannot Read 2D Codes:
Lacks vertical data capture capability.
Area Image Sensor (2D Imaging):
Uses a camera or CCD/CMOS sensor to capture the entire barcode image, then decodes the matrix.
Omnidirectional Reading:
Can read 2D codes at any angle (even if rotated or tilted).
1D Compatibility:
Can decode 1D barcodes by processing them as a single-line image (requires hybrid mode support).
3. Automatic Differentiation Mechanism
Modern scanners (e.g., supermarket POS systems, mobile apps) automatically distinguish barcode types by:
1.Initial Image Analysis:
Detects whether the pattern matches 1D stripes or 2D matrix features.
Example: QR codes have three alignment markers ("finder patterns").
2.Decoding Attempts:
First tries 1D decoding; if it fails, switches to 2D algorithms.
3.Hardware Support:
High-end scanners are labeled "1D/2D Dual Mode" or "Omnidirectional."
4. How Users Can Identify Scanner Type
Laser Scanner → Only supports 1D barcodes.
Camera/Red LED Imager → Likely supports 2D barcodes.
Product Manual:
Check for terms like "2D Imager" or "QR Code Compatible."
5. Special Cases
Stacked 1D Barcodes (e.g., PDF417):
Appears as multi-layer 1D but is technically a 2D code, requiring a 2D scanner.
Mobile Scanning Apps:
Default support for 1D/2D (e.g., WeChat Scan), using adaptive algorithms.
Summary
1D Scanners: Use lasers/linear sensors—only read stripes.
2D Scanners: Use cameras—support both 1D and 2D.
Auto-Detection: Achieved via pattern recognition + multi-mode decoding.
For purchasing, choose a "2D Imager" scanner for universal compatibility!