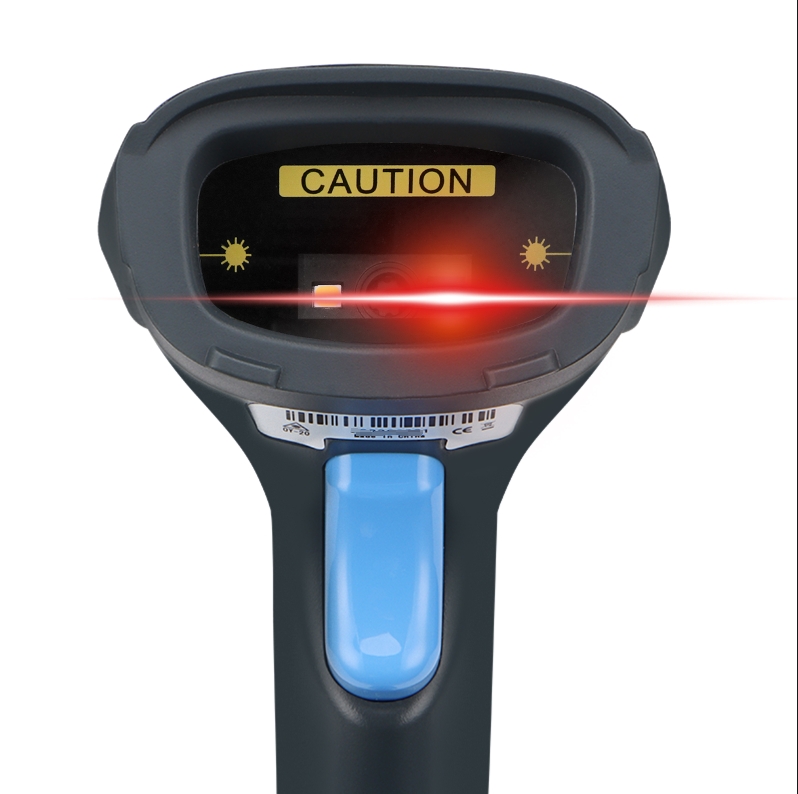
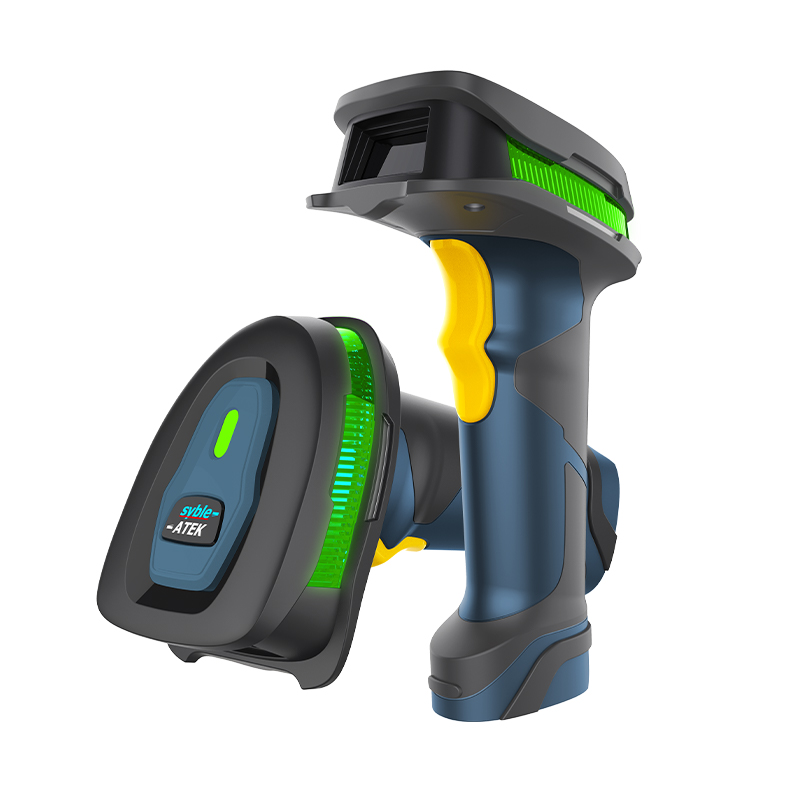
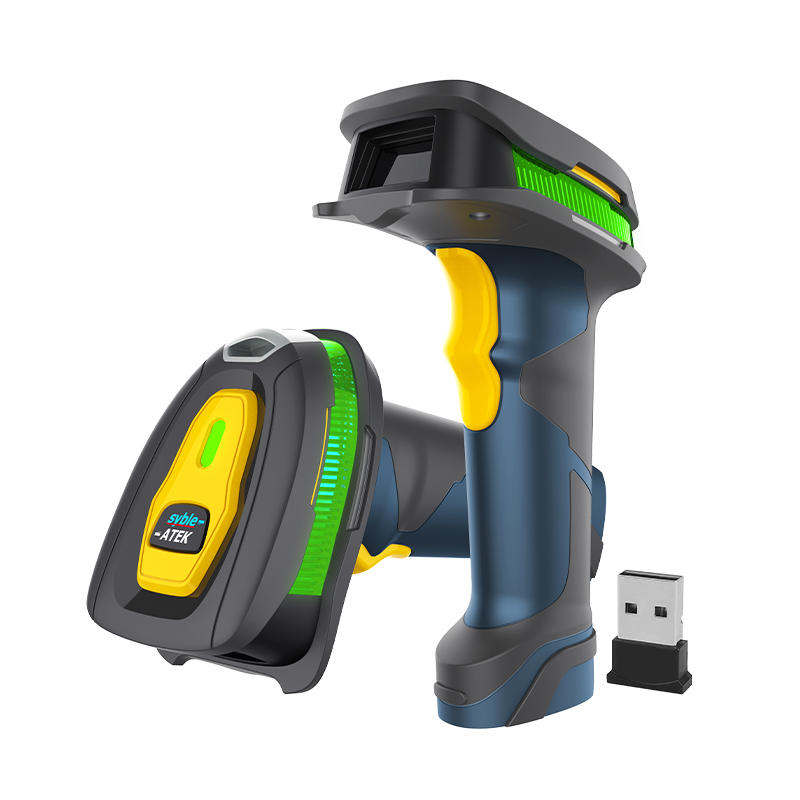
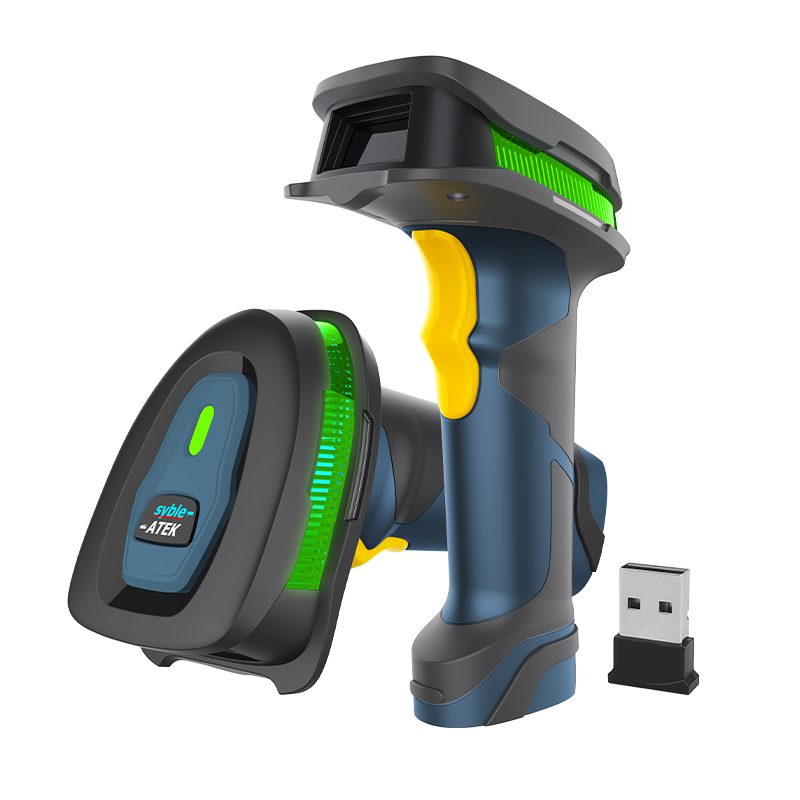
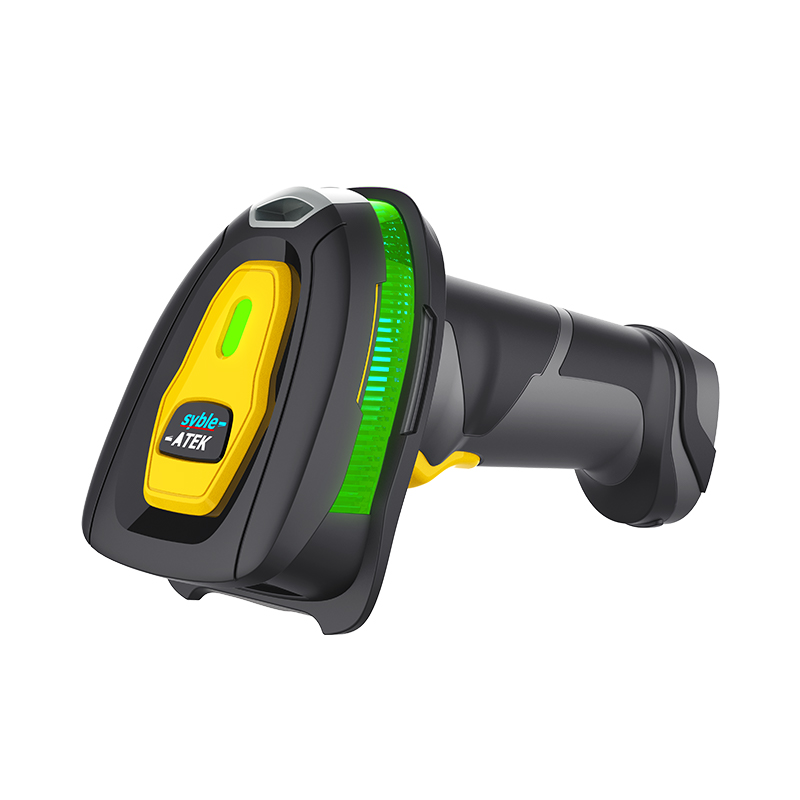
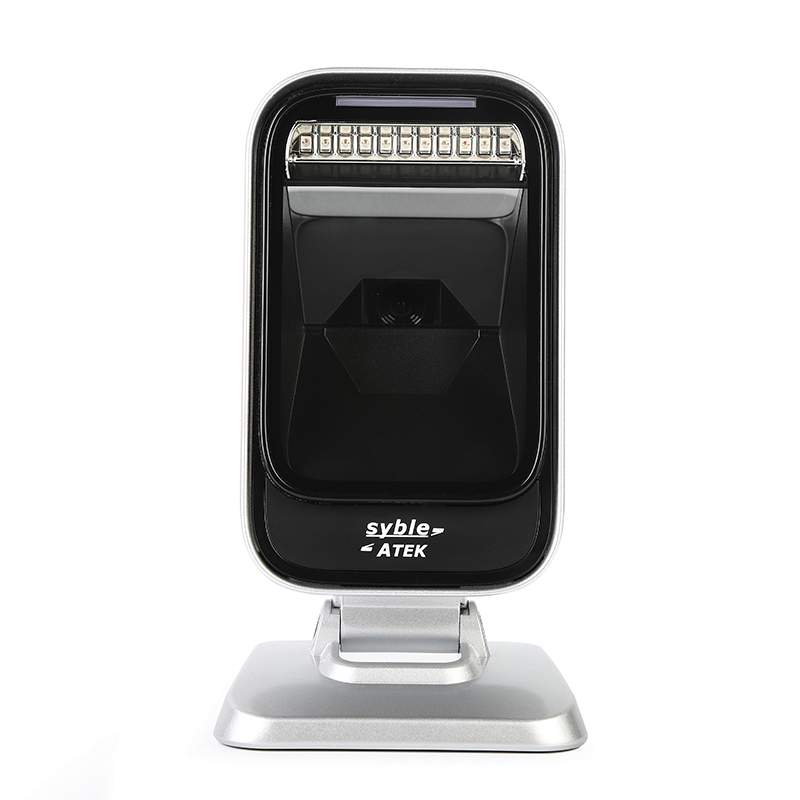
Advantages:
1.High Accuracy – Laser scanners provide precise scanning, reducing errors in reading barcodes.
2.Long Scanning Range – Can read barcodes from a greater distance (up to several feet) compared to other types.
3.Fast Scanning Speed – Decodes barcodes almost instantly, improving efficiency in retail and logistics.
4.Durability – More robust and resistant to wear and tear, making them suitable for industrial environments.
5.Works Well with Poor-Quality Barcodes – Can read damaged, faded, or poorly printed barcodes better than some alternatives.
6.No Need for Direct Contact – Scans without requiring physical touch, which is useful for hygiene-sensitive environments.
Disadvantages:
1.Cannot Read 2D Barcodes – Traditional laser scanners only read linear (1D) barcodes, not QR codes or matrix codes.
2.Sensitive to Reflective Surfaces – Glare or shiny packaging can interfere with scanning.
3.Moving Parts – Contains internal mirrors and lasers, making them more prone to mechanical failure over time.
4.Higher Cost – Generally more expensive than basic LED barcode scanners.
5.Limited Angle Scanning – Requires proper alignment; scanning at awkward angles may fail.
6.Not Ideal for Mobile Use – Typically bulkier than some modern alternatives (e.g., smartphone-based scanners).
Best Use Cases:
Retail checkout counters
Warehouse and inventory management
Industrial and manufacturing environments