Barcode scanners are essential tools in modern business operations, enabling efficient data capture and management. From retail to healthcare, these devices streamline processes, reduce errors, and enhance productivity. This article explores the different types of barcode scanners, their technologies, and their applications across various industries.
Types of Barcode Scanners
1. Pen-Type or Wand-Type Readers
Technology: Pen-type readers consist of a light source and a photodiode at the tip of a pen. The user must swipe the pen across the barcode at a consistent speed to read it.Applications: These scanners are cost-effective and primarily used in small-scale businesses and basic inventory management due to their simplicity and low cost.
2. Laser Barcode Scanners
Technology: Laser scanners use a laser beam directed by a deflection mirror to read barcodes. They are highly accurate and can read barcodes from a distance.Applications: Commonly used in retail environments, particularly at point-of-sale (POS) systems, for their speed and reliability in reading 1D barcodes like UPC and EAN codes.
3. CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) Barcode Scanners
Technology: CCD scanners use an array of tiny light sensors to capture barcode images. They excel at reading 1D barcodes up close.Applications: Often used in document scanning, library systems, and retail POS systems. They are not suitable for long-range scanning or damaged barcodes.
4. 2D Imaging Barcode Scanners
Technology: These scanners use a camera to capture images of barcodes, allowing them to read both 1D and 2D barcodes, including QR codes and data matrix codes.Applications: Widely used in healthcare, manufacturing, and logistics due to their versatility in capturing various data formats within a single scan.
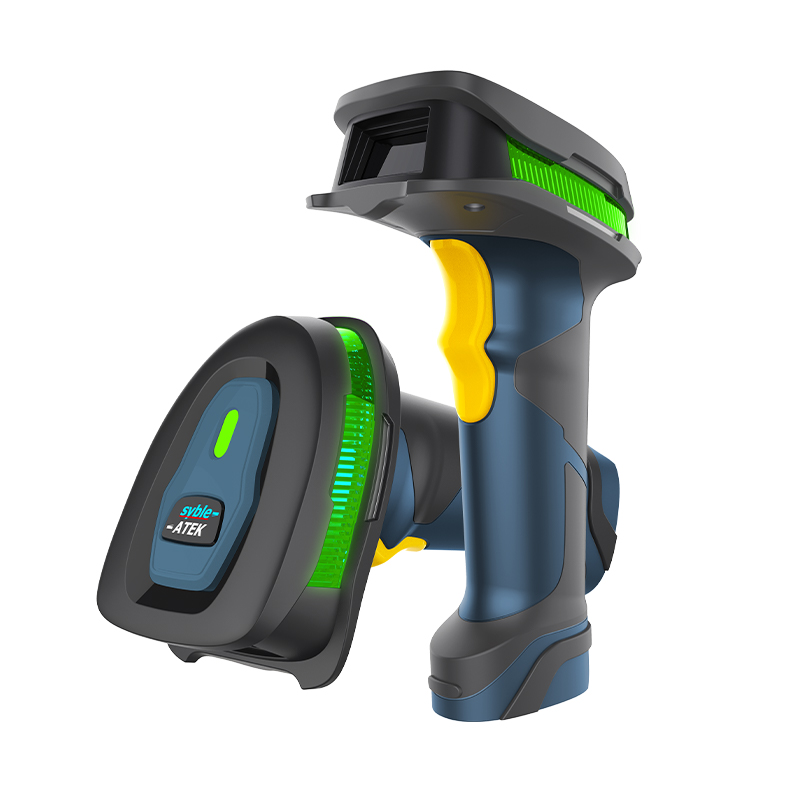
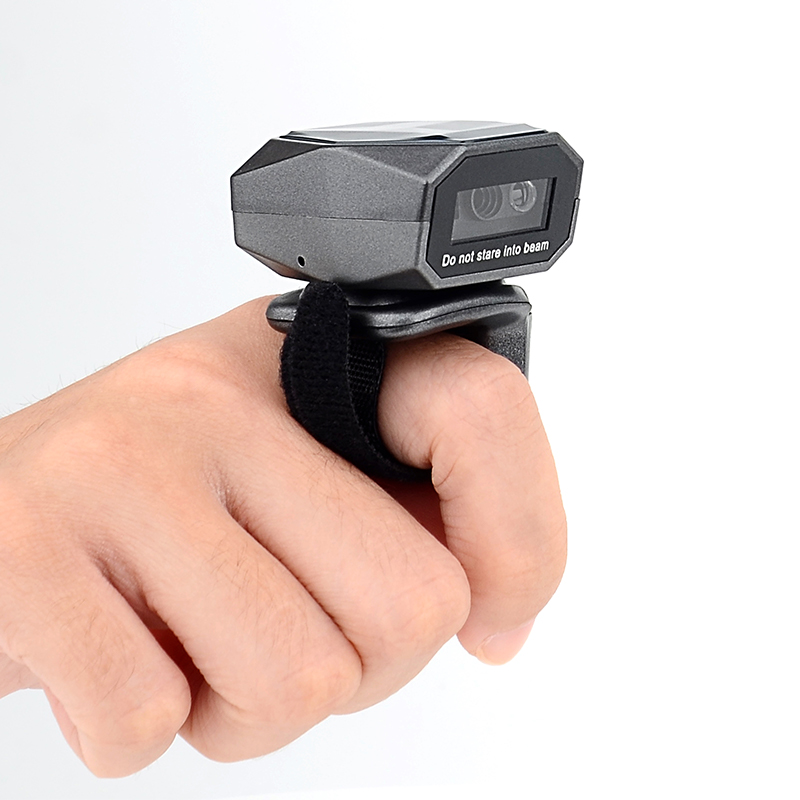
5. Wireless Barcode Scanners
Technology: Operate via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, providing mobility and flexibility.Applications: Ideal for warehouses and distribution centers, allowing operators to move freely while scanning items.
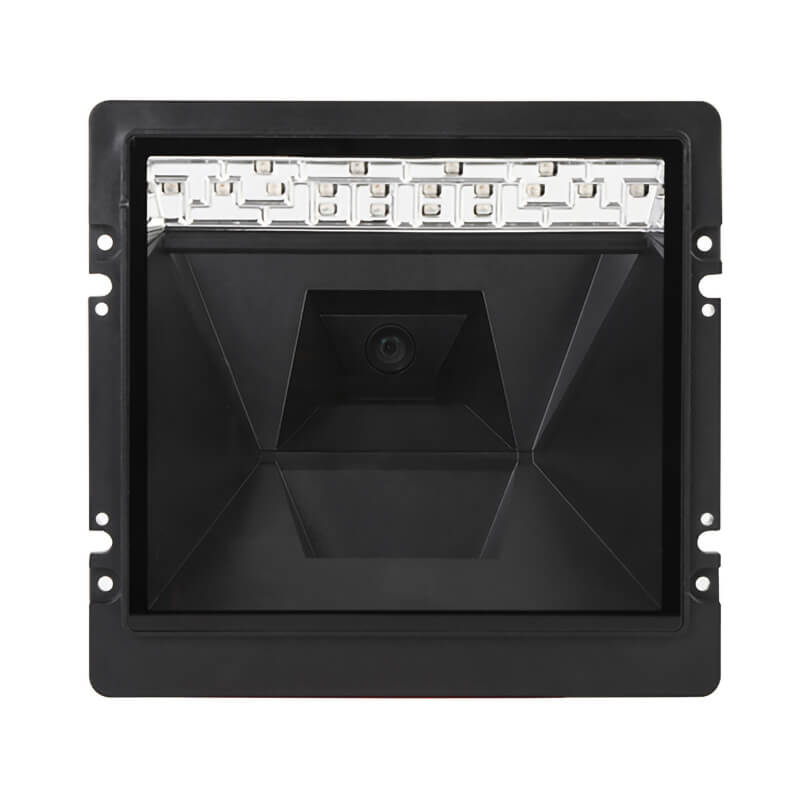
6. Fixed-Mount Barcode Scanners
Technology: Stationary devices that automatically scan barcodes as items pass by.Applications: Used in manufacturing facilities, retail store entrances, and conveyor belts for high-volume data capture.
7. Rugged Barcode Scanners
Technology: Designed to withstand harsh conditions, including dust, moisture, and drops.Applications: Prevalent in industries like construction, agriculture, and field service where environmental durability is crucial.
Applications of Barcode Scanners
Retail
Barcode scanners are indispensable in retail for inventory management, price checking, and checkout processes. They help reduce human errors, speed up transactions, and provide real-time inventory updates.
Healthcare
In healthcare, barcode scanners ensure accurate patient identification, medication administration, and specimen tracking. They help prevent medication errors and improve patient safety.
Manufacturing
Manufacturers use barcode scanners to track raw materials, work-in-progress items, and finished goods. This enhances production efficiency, reduces errors, and ensures accurate inventory management.
Logistics and Warehousing
Barcode scanners streamline operations in logistics and warehousing by tracking shipments, managing inventory, and optimizing storage locations. They help reduce picking errors and improve order accuracy.
Hospitality
In the hospitality industry, barcode scanners are used for inventory management, tracking linens, and managing equipment. They help improve resource utilization and reduce costs.
Benefits of Barcode Scanners
Accuracy: Reduces human errors in data entry.
Efficiency: Speeds up processes like checkout and inventory management.
Cost-Effective: Reduces labor costs and improves operational efficiency.
Real-Time Data: Provides up-to-date information on inventory and sales.
Limitations of Barcode Scanners
Cost: Initial investment can be high, especially for advanced models.
Training: Employees need proper training to use scanners effectively.
Dependency on Barcodes: Scanners are useless without barcoded items, and damaged barcodes can cause issues.
Conclusion
Barcode scanners are vital tools across various industries, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. By understanding the different types of barcode scanners and their applications, businesses can choose the right technology to meet their specific needs. As technology advances, barcode scanners will continue to evolve, offering even greater capabilities and benefits.